The reflection of human intelligence in machines, usually through computer systems, is known as artificial intelligence (AI). These systems can carry out tasks like speech recognition, visual perception, language translation, and decision-making that often need human intelligence. AI includes several subfields, such as robotics, computer vision, machine learning, natural language processing, and expert systems. The goal of artificial intelligence (AI) is to build systems that can work independently and accurately than humans.
History of Artificial Intelligence:
The timeline of artificial intelligence (AI) extends over numerous years and is identified by notable accomplishments and vital moments.
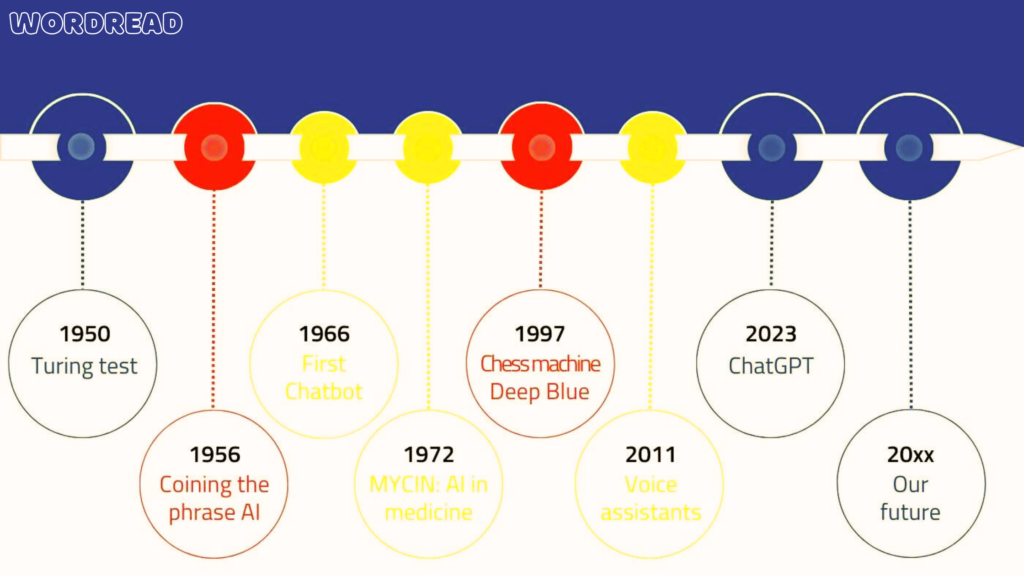
⦁ Early Concepts (1940s–1950s):
⦁ Scientists like Alan Turing, who created the Turing Test in 1950 as a gauge of a machine’s intelligence. He supported the development of the idea of artificial intelligence in the 1940s and 1950s.
⦁ The term “artificial intelligence” originated in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where scientists gathered to explore the objective of building robots capable of functioning similarly to humans.
⦁ Initial Developments (1950s–1960s):
⦁ Symbolic AI reflects human thought through rules and symbols, which emerged in the 1950s and 60s. The beginning of problem-solving skills was shown by programs such as a General Problem Solver and the Logic Theorist.
⦁ The Logic Theorist, the first artificial intelligence application designed by Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon in 1956 highlighted the potential of AI.
⦁ Cold War AI (1970s–1980s):
⦁ Despite early interest, technical obstacles and impractical expectations led artificial intelligence (AI) development to stop in the 1970s and 1980s. Known as the “Cold War AI,” this period saw a fall in attention and budget for AI research.
⦁ During this time, professional systems became more common. They employed rules that simulated human skills in particular fields.
⦁ Progress and Revival (1990s–Present):
⦁ Due to computing power and methods developments, passion for AI saw a rise in the 1990s.
⦁ Deep learning techniques, especially those involving artificial brains and statistics are of increasing importance in AI research.
⦁ AI systems’ powers were shown by significant events like Google’s AlphaGo defeating Go world champion Lee Sedol in 2016 and IBM’s Deep Blue defeating world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997.
⦁ As engineered suggestions, virtual assistants, and automated vehicles were developed, artificial intelligence technologies became more common in our daily lives.
⦁ Difficulties with employment shifting, disbenefit in algorithms, and security concerns are just some of AI’s social and cultural effects.
Pros and Cons of Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial intelligence (AI) has many benefits as well as drawbacks. These are some of the main benefits and drawbacks:
⦁ Pros:
⦁ AI makes it possible to remotely operate jobs, which reduces the need for human labour and enhances revenue across a variety of sectors like customer service and manufacturing.
⦁ Artificial intelligence (AI) can increase productivity by automating repetitive tasks and simplifying procedures. This allows humans to focus on more innovative and tactical duties.
⦁ AI systems can easily and securely examine vast amounts of data. It also assists businesses and organizations in making accurate choices based on designs and ideas.
⦁ AI systems can carry out tasks with a high level of consistency and accuracy which lowers errors and increases results in tasks like inspection, budgeting, and medical diagnostics.
⦁ Systems driven by AI can work repeatedly, without boring out or offering breaks, providing users unlimited help and guidance.
⦁ AI promotes scientific discovery in sectors like medicine advancement, material research, and astronomers as well as development by enabling the investigation of new solutions to difficult issues.
⦁ Cons:
⦁ AI (automation of jobs) has the potential to displace workers, especially in posts needing regular or repeated duties. The lack of employment and financial trouble may result from this.
⦁ Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms have the potential to boost or magnify the prejudicial beliefs found in the training data, which could result in unfair hiring, funding, or other acts.
⦁ Concerns around privacy and illegal access to sensitive data are driven by the idea that AI systems usually rely on huge amounts of personal data to work properly.
⦁ The usage of AI in several settings, including self-powered weapons, tracking, and key decision-making in the criminal justice and healthcare sectors, presents ethical questions.
⦁ AI’s use in social evaluation, military applications, and monitoring creates ethical questions. It determines a balance between its advantages and moral issues.
⦁ The inequitable distribution of AI’s benefits may increase economic inequality. Certain populations or locations may not have equal access to AI technologies and their benefits.
Artificial Intelligence Death Calculator:
An artificial intelligence death calculator is a device that analyzes a person’s probability of passing away based on a variety of lifestyle and health characteristics using AI algorithms. These calculators usually examine data such as age, sex, medical history, and lifestyle behaviors (e.g., smoking, alcohol intake, physical activity). It occasionally genetic information to produce an estimate of life duration or mortality risk within a given timeframe. Another name for an AI death calculator is a mortality risk prediction model.

How does an AI Death Calculator work?
⦁ The death calculator collects information from the person, usually consisting of age, gender, weight and height (to calculate BMI), blood pressure, cholesterol levels, smoking status, physical activity level and medical history (e.g., diabetes, heart disease).
⦁ Statistical models and machine learning methods are used by the AI system to process the data. It finds trends and risk factors by comparing the user’s data with big databases of medical data.
⦁ AI death calculators use models and data that are currently available, therefore their forecasts could not be entirely true and relevant to every person.
⦁ Users need to use precautions while exposing private health information. It is essential to make sure that the calculator follows data protection laws (such as GDPR and HIPAA).
⦁ Finding out how likely you will pass away can be depressing. It’s critical that consumers utilize these tools appropriately and can get help when they need it.
⦁ AI models might inherit biases from the data they are trained on, certain users may receive unfavorable predictions.
Popular AI Death Calculator:
Artificial intelligence algorithms are employed by various death calculator programs and mortality prediction models to determine the possibility of developing specific diseases or dying within a specified time. There are the following popular AI Death Calculator:

⦁ QRISK:
A popular technique for calculating the chance of getting cardiovascular disease in the UK, also known as CVD, over a given length of time is called QRISK. It considers many risk factors, including age, gender, ethnicity, status as a smoker, blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and family history of cardiovascular disease.
⦁ Framingham Risk Score:
A well-known algorithm for estimating the 10-year risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) based on a number of risk variables is the Framingham Risk Score. It takes into account variables including blood pressure, smoking status, age, gender, total and HDL cholesterol levels, and blood pressure.
⦁ AHEAD Model:
A mortality prediction model known as AHEAD (Aging, Health, Education, and Demographics) was created expressly to forecast the probability of death among older persons in the US. The estimation of death probability over a certain time horizon is achieved by including multiple demographic, socioeconomic, and health-related factors.
AI Chatbot:
A computer program or AI application is called an AI chatbot. Sometimes, it is referred to as a chatbot or conversational agent that is made to mimic human-like discussions with users through text or audio interactions. These chatbots interpret user inputs and provide pertinent responses by using artificial intelligence techniques like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and occasionally even deep learning.
How does an AI Chatbot work?
⦁ NLU algorithms are used by chatbots to read and understand user messages. This requires splitting the input language into relevant parts, like entities, intents, and context.
⦁ The chatbot uses dialogue management to understand the user’s message, maintain context, manage conversation flow, and select the most relevant response based on the current interaction.
⦁ The chatbot uses machine learning techniques to either produce text or speech output for communication or pre-program it. It’s all done after determining the proper response.
⦁ AI chatbots use machine learning techniques to improve over time. It enhances their understanding and responses based on user interactions and feedback.
Types of AI Chatbot:
There are the following types of AI Chatbot that are discussed as follow:

⦁ Ruled-based chatbots:
These chatbots function according to preset norms and patterns. They interpret user inputs and provide replies by adhering to a set of instructions. Rule-based chatbots are most suitable for handling straightforward, organized interactions, although they usually have fewer capabilities.
⦁ Machine learning Chatbots:
Machine learning chatbots use algorithms to analyze data. The users understand complex language patterns, and adapt behavior based on training data, making them more flexible and capable of handling various tasks.
⦁ Hybrid Chatbot:
Hybrid chatbots take advantage of the positive aspects of both machine learning and rule-based systems. When we are dealing with situations that are more unclear or new, they could turn to machine learning models instead of guidelines.
Chatbots are used in educational environments to offer individual learning experiences, teach students in language, and more. AI chatbots are a big help in increasing productivity, bettering user experiences, and automating a lot of different jobs in a variety of fields and businesses.


36 Comments
Your posts are always so informative and well-written.
duyung303 https://womenshealthdynamics.com/duyung-303-19/
Thanks for another great article. The place else may anybody
get that kind of info in such a perfect manner of writing?
I’ve a presentation next week, and I’m on the look for such
info.
good to hear that you like it
visa4d
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having problems locating
it but, I’d like to shoot you an e-mail. I’ve got some recommendations for your
blog you might be interested in hearing. Either
way, great website and I look forward to seeing it expand over time.
you can mail on wordread.com@gmail.com
zara4d
When I look at your website in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other
then that, excellent blog!
I’ll try to fix this issue you no need to worry and thanks for your help
Regards
bos88 bos88
You can definitely see your expertise in the work you write.
The sector hopes for more passionate writers such as you
who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always follow your heart.
Appreciation to my father who told me on the topic
of this website, this website is in fact awesome.
If some one wants expert view about blogging then i suggest him/her to pay a quick visit this weblog, Keep up the fastidious work.
Pingback: Evolving E-Commerce Logistics: The Role of Autonomous Drones and AI in Future Deliveries - YOUR DAILY DOSE OF INSIGHTS
Great post. I am going through many of these issues as well..
If you want to grow your know-how just keep visiting this website and be updated with the most recent news posted here.
Currently it looks like Expression Engine is the top blogging platform available right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your
blog?
What i do not realize is in fact how you are not really much more neatly-liked than you may be now.
You’re so intelligent. You know thus considerably relating to
this matter, produced me personally consider it from a lot of
varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t interested until it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga!
Your individual stuffs great. At all times deal with
it up!
What’s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It positively useful and it has
helped me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & help different customers like its helped
me. Good job.
Hey would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re working with?
I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different internet browsers and
I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most.
Can you recommend a good hosting provider at a honest price?
Kudos, I appreciate it!
Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did
you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a
few simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out.
Please let me know where you got your theme. Appreciate it
What’s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have
discovered It positively useful and it has helped me out loads.
I am hoping to give a contribution & help other customers
like its helped me. Great job.
It is truly a nice and useful piece of info. I’m satisfied that you simply shared this helpful info with us.
Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the net the easiest thing to be aware of.
I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly don’t know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side effect ,
people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more.
Thanks
Pingback: 8 actions that show Cats have their own unique Logic - Wordread
I like it when individuals get together and share thoughts.
Great blog, keep it up!
I think this is among the most significant information for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on few general things,
The web site style is great, the articles is really nice :
D. Good job, cheers
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Well written!
Hello very cool site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Superb ..
I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds also? I’m happy to seek out a lot
of helpful information right here within the publish, we need work out extra
techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . .
. .
Your method of describing all in this article is actually good,
every one be able to effortlessly know it, Thanks a lot.
It’s not my first time to pay a quick visit this website, i am visiting this site dailly and take pleasant facts from
here daily.
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog site?
The account aided me a acceptable deal. I were tiny bit
acquainted of this your broadcast offered vibrant transparent concept
Very nice write-up. I absolutely appreciate this website.
Keep it up!
I feel that is among the most vital information for me.
And i’m glad studying your article. However want to observation on few
basic things, The website taste is ideal, the articles is in reality great
: D. Good task, cheers
Great post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed!
Extremely helpful information specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such information much.
I was looking for this certain information for a long time.
Thank you and best of luck.
Ahaa, its good discussion concerning this piece of writing here at this weblog, I have read all that, so at this time me also commenting here.
Hello there, I do believe your website might be having
internet browser compatibility issues. When I look at your site in Safari, it looks fine however, when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues.
I merely wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Apart from that, wonderful blog!
I visit everyday a few blogs and websites to read content, however this blog
provides quality based articles.
I was able to find good information from your content.